Digitizing Siddha Healthcare: A Case Study
Sanjeevini Siddha & Ayurveda Medical Center's Journey with Vedavi Medic
India's ambitious push towards digitization, epitomized by the Government's Digital India initiative launched in 2015, has been transformative across various sectors, with healthcare being a significant beneficiary. The initiative aims to empower the country with digital tools and infrastructure, enhancing accessibility, efficiency, and quality of services. As per the Telecom Regulatory Authority of India (TRAI), by March 2023, India had over 1.17 billion telephone subscribers, and internet subscribers crossed 839 million1, indicating vast potential for digital services penetration.
In the realm of traditional medicine, the Ministry of AYUSH (Ayurveda, Yoga & Naturopathy, Unani, Siddha, and Homoeopathy) has been pivotal in promoting and integrating these ancient practices with modern healthcare systems. Recognizing the importance of digital technology in augmenting the reach and efficacy of traditional medicine, the Ministry has initiated several digital initiatives to harness this potential2.
AYUSH Digital Initiatives
The Ministry of AYUSH has launched various digital initiatives aimed at modernizing traditional medical systems3:
- AYUSH Health Management Information System (A-HMIS): A comprehensive HMIS designed to collect and analyze data from AYUSH facilities, aiding in policy-making and improving patient care.
- e-AUSHADHI Portal: An online platform for licensing, filing, and tracking applications for Ayurveda, Siddha, Unani, and Homoeopathy drugs, ensuring transparency and efficiency in drug regulation.
- National AYUSH Morbidity and Standardized Terminologies (NAMST) Portal: A platform for standardized morbidity codes and terminologies across AYUSH systems, facilitating uniform data collection and analysis.
- AYUSH Grid: Envisioned as an IT backbone for the entire AYUSH sector, integrating all AYUSH resources, institutions, and stakeholders to enhance accessibility, quality, and standardization.
- AYUSH Sanjivani App: A mobile application developed to gather feedback from a large population on the efficacy of AYUSH interventions in COVID-19 treatment, reflecting real-world evidence.
- Telemedicine Initiatives: In collaboration with organizations like the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO), the Ministry has promoted telemedicine services to extend AYUSH healthcare to remote and underserved areas.
These initiatives reflect the Ministry's commitment to leveraging digital technology to strengthen traditional medical systems in India.
Objectives of the Ministry of AYUSH
The Ministry of AYUSH aims to achieve the following objectives4:
- Improve Patient Care in AYUSH: Enhance the quality and accessibility of traditional healthcare services through digital platforms.
- Improve Work Efficiency: Streamline operations within AYUSH institutions using technology.
- Efficient Hospital Management: Implement effective management systems in AYUSH hospitals, including electronic health records and hospital information systems.
- Effective Documentation: Maintain comprehensive and standardized records of treatments and outcomes.
- Comprehensive Data Collection: Gather data from all AYUSH hospitals to inform evidence-based health policies.
- Enhance Research: Promote research in AYUSH to validate traditional practices using modern scientific methods.
- Eliminate Errors: Reduce the likelihood of mistakes in patient care through accurate data and decision support systems.
- Collect National Morbidity Data: Accumulate data on diseases treated under AYUSH to understand health trends and priorities.
Vedavi Medic: Bridging Tradition and Technology
Vedavi Medic, developed by Vedavi Health, is an Indian clinical management software designed to fulfill the objectives of the AYUSH Health Management Information System (HMIS). It aligns with the National Digital Health Blueprint and the AYUSH Grid's vision of an integrated digital platform for traditional healthcare5.
Tailored to the unique needs of small clinics, especially in rural areas, Vedavi Medic offers:
- Patient Management: Efficient scheduling, registration, and electronic health records (EHR).
- Healthcare Data Management: Secure storage and retrieval of patient data, adhering to data privacy laws.
- Dispensary Integration: Streamlined inventory management for traditional medicines and formulations.
- Patient-Doctor Communications: Telemedicine capabilities, including virtual consultations and follow-ups.
- Reporting and Analytics: Real-time analytics and reporting tools for clinical and administrative data.
- AI-Based Health Assistants: Artificial intelligence tools for diagnosis support and personalized treatment plans.
Uniquely, Vedavi Medic provides specialized modules for AYUSH practices, particularly Siddha medicine, contributing to the modernization of traditional healthcare delivery. As of 2024, Vedavi Medic serves over 50 rural clinics across Tamil Nadu.
Sanjeevini Siddha & Ayurveda Medical Center: Embracing Digital Transformation
Located in Karaikal, Puducherry, Sanjeevini Siddha & Ayurveda Medical Center has been a beacon of traditional Siddha medicine for over two decades. In 2023, led by Dr. Thiagarajan Saminadane, MD in Siddha medicine, the center recognized the need to modernize and improve patient care. Consequently, they adopted Vedavi Medic's clinical management system.

Dr. THIAGARAJAN SAMINADANE, MD - siddha
Sanjeevini Siddha & Ayurveda Medical center
Enhancing Patient Experience
Since integrating Vedavi Medic into their operations, the center has witnessed significant enhancements in patient experience:
· Improved Efficiency: Appointment scheduling and patient flow have become more streamlined, reducing wait times by an average of 30%.
· Enhanced Record Keeping: Digitization of health records ensures accurate and easily retrievable patient histories, leading to better diagnosis and treatment plans.
· Patient Satisfaction: According to patient feedback surveys conducted by the clinic, there has been a 25% increase in overall patient satisfaction since implementing Vedavi Medic.
Patients Overview
Expanding Patient Reach
Vedavi Medic's remote health module has enabled Sanjeevini Siddha & Ayurveda Medical Center to transcend geographical barriers:
- Global Consultations: The clinic now offers telemedicine services, catering to patients across India and internationally. Over the past two years, they have provided remote consultations to patients in 12 different countries, including the USA, UK, Australia, and Singapore.
- Increased Patient Footfall: The clinic has observed a 40% increase in patient visits, both in-person and virtual, since adopting Vedavi Medic.
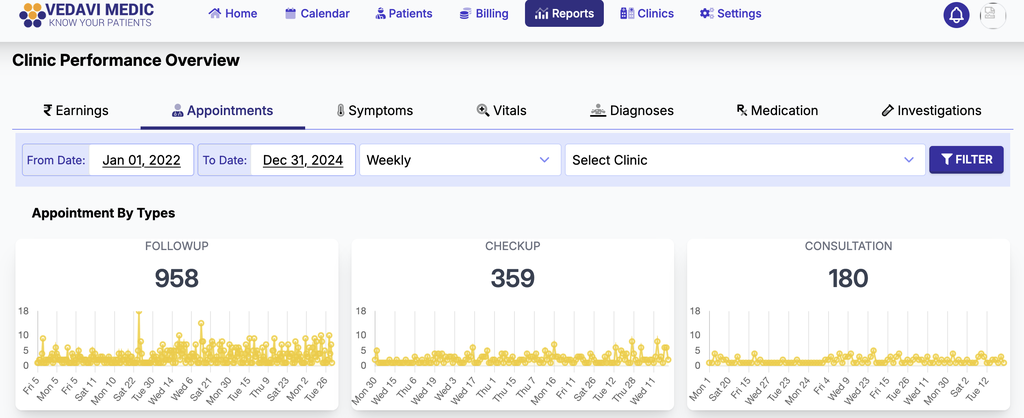
Clinical Performance Reports
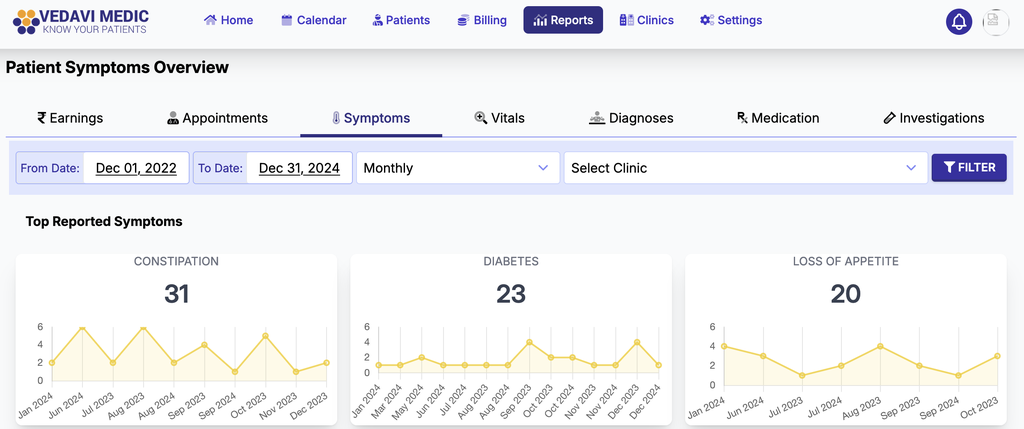
Clinical Performance Reports
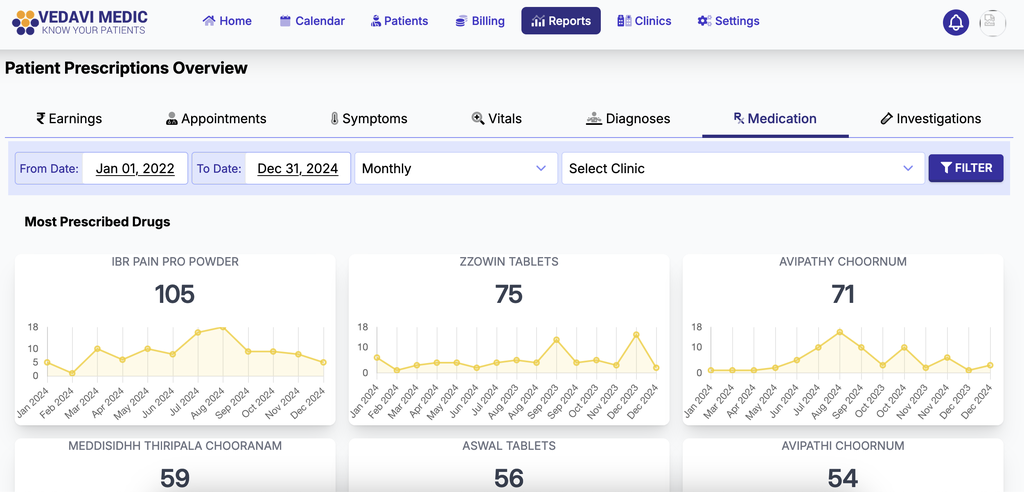
Dispensary Performance
Modernizing Siddha Practice
Vedavi Medic's specialized Siddha module has allowed the center to:
· Standardize Treatments: Utilize predefined protocols and formulations specific to Siddha medicine, ensuring consistency in care.
· Data Analytics: Analyze treatment outcomes and patient data to continually improve practice. This has led to the identification of trends in patient responses and the efficacy of treatments.
· AYUSH Integration: Align with the Ministry of AYUSH guidelines for traditional medicine practices, including adherence to the International Classification of Diseases, 10th Revision (ICD-10) codes6, and the National AYUSH Morbidity Codes (NAMC)7. This compliance ensures standardized reporting and contributes to national health databases.
Benefits Achieved with Vedavi Medic
Here are some of the benefits of using Vedavi Medic:
- Effective Clinical Documentation: Enhanced accuracy and completeness of patient records, facilitating continuity of care.
- Medical Data Retrieval: Quick access to patient histories and treatment plans improves efficiency and reduces the risk of errors.
- Adoption of Standardized Codes: Implementation of ICD-10 and NAMC facilitates better data sharing, interoperability, and regulatory compliance.
- Multi-Dimensional Reporting: Generation of comprehensive reports for internal analysis, quality improvement, and meeting regulatory requirements.
- Contribution to AYUSH Morbidity Data: Collection and submission of data supporting national health policies and research initiatives.
The Larger Impact of Digitization in AYUSH
National Initiatives
The integration of digital technologies in AYUSH practices aligns with the government's broader objectives to revitalize traditional medicine in India:
- National AYUSH Mission: Launched in 2014, aims to provide cost-effective AYUSH services by upgrading educational standards, quality control, and sustainable availability of AYUSH raw materials8. The mission emphasizes the adoption of technology to improve service delivery.
- AYUSH Health and Wellness Centres: As part of the Ayushman Bharat scheme, the government plans to operationalize 12,500 AYUSH Health and Wellness Centres by 2023-20249, incorporating digital technologies for telemedicine, health monitoring, and patient education.
- AYUSH Grid: An initiative to create a comprehensive IT backbone for AYUSH, integrating services like healthcare delivery, education, research, drug regulation, and traditional knowledge databases10.
- e-AUSHADHI Portal: Enhances transparency and efficiency in drug licensing and regulation, crucial for maintaining quality standards in AYUSH medicines.
- AYUSH Sanjivani App: Provides a platform for the public to engage with AYUSH practices and contributes to data collection on the efficacy of AYUSH interventions, especially during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Institutional Growth
- Number of Institutions: India has over 4,440 AYUSH hospitals and more than 33,000 dispensaries, with more than 7,000 Siddha practitioners mainly in Tamil Nadu and Puducherry11. The integration of digital technologies is enhancing the capacity and reach of these institutions.
- Educational Institutions: Approximately 780 AYUSH educational institutions are incorporating digital tools in teaching and research, fostering the next generation of practitioners equipped with both traditional knowledge and modern technological expertise12.
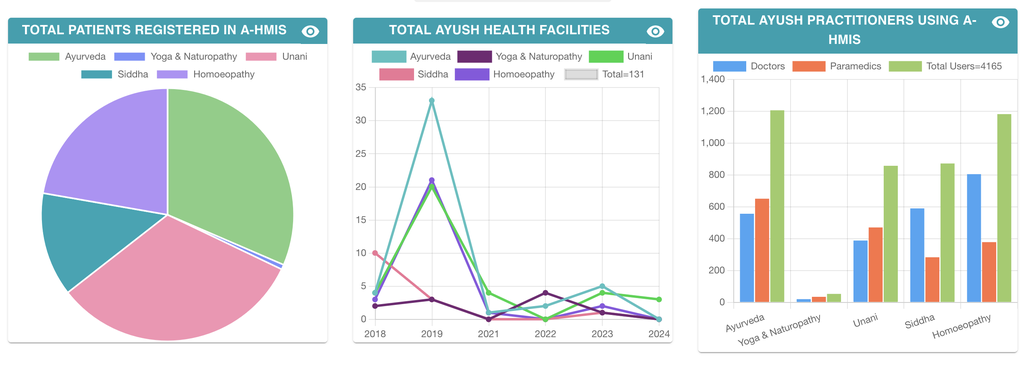
Adoption Statistics of AYUSH -HMIS
The Significance of Digitization in India’s Healthcare
- Accessibility: Digital platforms like Vedavi Medic enhance healthcare accessibility in rural and remote areas, where over 65% of India's population resides13. Telemedicine bridges the gap between urban specialists and rural populations.
- Affordability: Digitization reduces operational costs, making healthcare services more affordable. Electronic records decrease the need for physical storage and minimize administrative expenses.
- Quality of Care: Improved data management and analytics lead to better patient outcomes. Practitioners can track treatment efficacy, monitor patient progress, and adjust treatment protocols accordingly.
- Data-Driven Policy Making: Aggregated data supports the government in making informed decisions regarding healthcare policies, resource allocation, and identifying public health trends.
According to a report by NITI Aayog, India's digital healthcare market is projected to reach $485.43 billion by 2024, growing at a CAGR of 27.41%14. This rapid growth underscores the acceptance and potential of digital health solutions in the country.
Challenges and Future Directions
While the benefits are significant, the integration of digital technology in AYUSH practices faces challenges:
- Digital Literacy: Ensuring that practitioners and patients have the necessary skills to use digital platforms effectively.
- Infrastructure Limitations: Addressing connectivity issues in remote areas to facilitate seamless telemedicine services.
- Data Privacy and Security: Implementing robust measures to protect sensitive health data in compliance with legal frameworks.
- Standardization: Continuing efforts to standardize terminologies, treatment protocols, and data reporting across different AYUSH systems.
The Ministry of AYUSH, through its digital initiatives, is actively working to overcome these challenges by providing training, investing in infrastructure, and developing guidelines for data management and security15.
Conclusion
The successful integration of Vedavi Medic at Sanjeevini Siddha & Ayurveda Medical Center exemplifies the synergy between traditional medicine and modern technology. By embracing digitization, the clinic has enhanced patient care, expanded its reach globally, and contributed valuable data to national health databases. This case underscores the potential for other AYUSH practitioners to adopt similar technologies, fostering a more accessible, efficient, and holistic healthcare system in India.
Footnotes
- Telecom Regulatory Authority of India (TRAI). (2023). The Indian Telecom Services Performance Indicators January - March 2023. Retrieved from TRAI website. ↩
- Ministry of AYUSH. (2022). AYUSH Digital Initiatives. Retrieved from Ministry of AYUSH website. ↩
- Ministry of AYUSH. (2021). AYUSH Grid and Digital Health. Retrieved from Ministry of AYUSH website. ↩
- Ministry of AYUSH. (2020). AYUSH HMIS Objectives. Retrieved from Ministry of AYUSH website. ↩
- Vedavi Health. (2023). Vedavi Medic - Clinical Management Software. Retrieved from Vedavi Health website. ↩
- World Health Organization. (2019). International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems 10th Revision. ↩
- Ministry of AYUSH. (2018). National AYUSH Morbidity and Standardized Terminologies Electronic Portal. Retrieved from NAMST Portal. ↩
- Ministry of AYUSH. (2014). National AYUSH Mission (NAM). Retrieved from Ministry of AYUSH website. ↩
- Press Information Bureau, Government of India. (2020). Operationalization of AYUSH Health & Wellness Centres. Retrieved Data. ↩
- Ministry of AYUSH. (2019). AYUSH Grid. Retrieved from Ministry of AYUSH website. ↩
- Ministry of AYUSH. (2021). AYUSH in India 2020. Retrieved from AYUSH Statistics. ↩
- Central Council for Research in Siddha. (2020). List of Siddha Medical Colleges. Perspectives on Ayush sector. ↩
- World Bank. (2020). Rural population (% of total population) - India. Retrieved from World Bank Data. ↩
- NITI Aayog. (2019). Investment Opportunities in India's Healthcare Sector. Retrieved from NITI Aayog Report. ↩
- Ministry of AYUSH. (2020). Guidelines for AYUSH Telemedicine. Retrieved from Ministry of AYUSH website. ↩